Salivary Soluble CD40 Ligand Levels and Their Relationship to Periodontal Markers in Patients with Periodontitis and/or Obesity: An Observational Case-Control Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54133/ajms.v5i.174Keywords:
Obesity, Periodontitis, Saliva, sCD40LAbstract
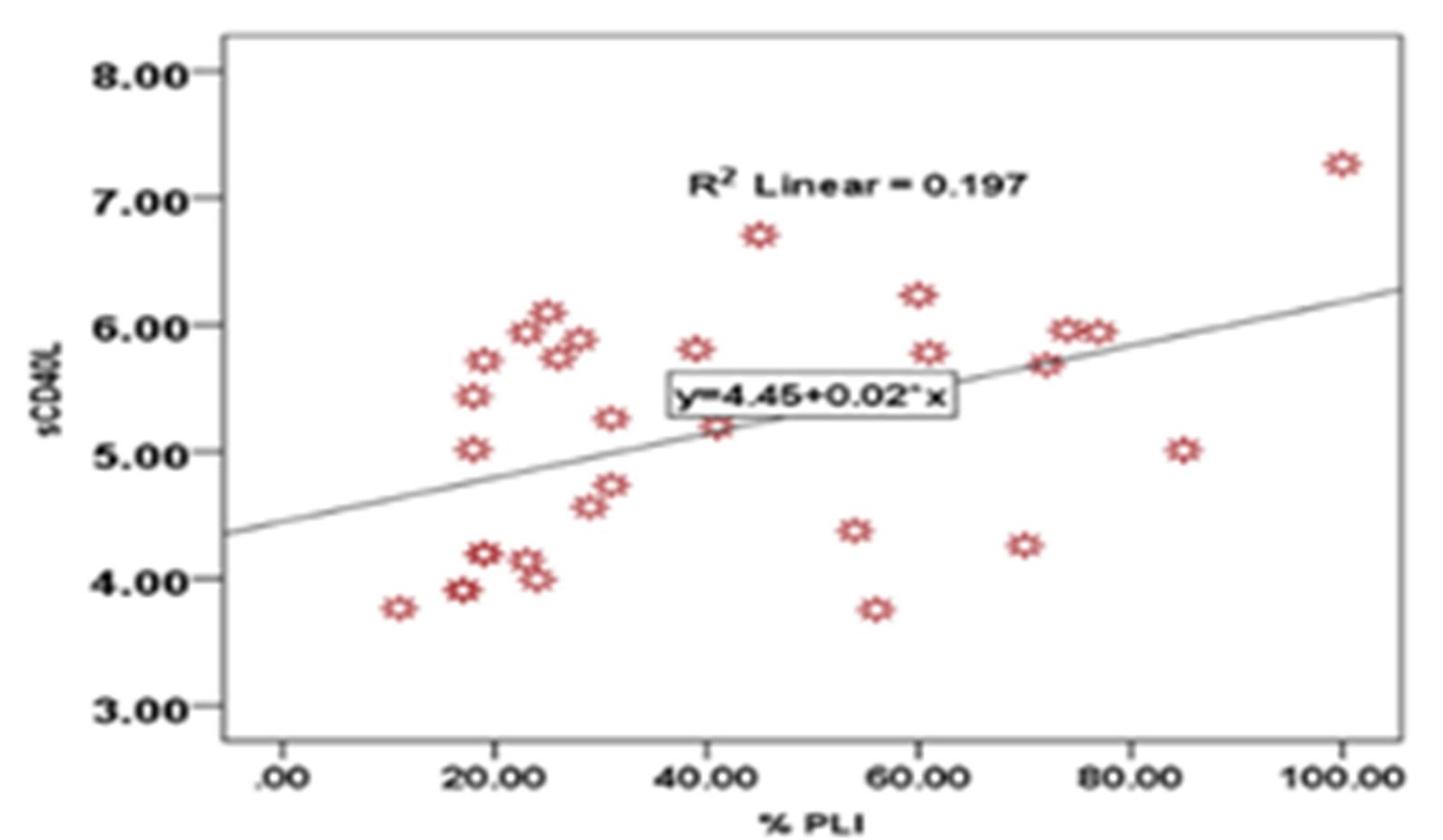
Background: sCD40L, a co-stimulatory molecule that activates T-helper cells, is one of many mediators that regulate the inflammatory conditions of periodontitis and obesity. Additionally, the association of this biomarker with periodontitis and obesity has not been robustly investigated. Objective: Evaluation of salivary levels of sCD40L in periodontitis and obese patients in comparison to healthy controls and their association with different periodontal parameters. Methods: 110 subjects were enrolled in this study. Salivary samples were obtained prior to the clinical examination. They were divided into four groups: the first group (20 subjects) was the control group; the second group (30 subjects) consisted of subjects with obesity (BMI≥30 kg/m2); the third group (30 subjects) consisted of subjects with periodontitis; and the fourth group (30 subjects) consisted of subjects with periodontitis and obesity. A periodontal examination was performed to report plaque index (PLI), bleeding on probing (BOP), probing pocket depth (PPD), and clinical attachment loss (CAL). Obesity was assessed using the body mass index (BMI). Results: Both periodontitis and obese patients demonstrated elevated salivary sCD40L levels compared to healthy subjects. sCD40L was positively correlated with PLI in periodontitis patients and with PPD in obese periodontitis patients. Conclusions: A significant association between sCD40L, periodontitis, and obesity was reported, implicating sCD40L's role in the pathogenesis of these conditions.
Downloads
References
Papapanou PN, Sanz M, Buduneli N, Dietrich T, Feres M, Fine DH, et al. Periodontitis: Consensus report of workgroup 2 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J Periodontol. 2018;89 (Suppl 1):S173-S182. doi: 10.1002/JPER.17-0721. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.17-0721
Silva N, Abusleme L, Bravo D, Dutzan N, Garcia-Sesnich J, Vernal R, Hernández M, Gamonal J. Host response mechanisms in periodontal diseases. J Appl Oral Sci. 2015;23(3):329-355. doi: 10.1590/1678-775720140259. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-775720140259
Bullon P, Newman HN, Battino M. Obesity, diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis and chronic periodontitis: a shared pathology via oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction? Periodontol. 2000. 2014;64(1):139-153. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2012.00455.x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0757.2012.00455.x
Franco R, Barlattani A, Perrone MA, Basili M, Miranda M, Costacurta M, et al. Obesity, bariatric surgery and periodontal disease: a literature update. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(9):5036-5045. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202005_21196.
Abas D, Eqbal G, Prevalence of obesity among adolescents at secondary schools in Kirkuk city. Iraqi Nat J Nurs Specialties. 2018;26:96-101. doi: 10.58897/injns.v26i2.175.
Jasim HM, Abdul Hussein HM, Al-Kaseer EA. Obesity among females in Al-Sader city Baghdad, Iraq, 2017. J Faculty Med Baghdad. 2018;60(2):105-107. DOI: https://doi.org/10.32007/19jfacmedbaghdad36.v60i2.15
Martinez-Herrera M, Silvestre-Rangil J, Silvestre FJ. Association between obesity and periodontal disease. A systematic review of epidemiological studies and controlled clinical trials. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2017;22(6):e708-e715. doi: 10.4317/medoral.21786. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.21786
Nascimento GG, Leite FR, Do LG, Peres KG, Correa MB, Demarco FF, et al. Is weight gain associated with the incidence of periodontitis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Periodontol. 2015;42(6):495-505. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12417. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12417
Pataro AL, Costa FO, Cortelli SC, Cortelli JR, Abreu MH, Costa JE. Association between severity of body mass index and periodontal condition in women. Clin Oral Investig. 2012;16(3):727-734. doi: 10.1007/s00784-011-0554-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-011-0554-7
Suvan J, Petrie A, Moles DR, Nibali L, Patel K, Darbar U, et al. Body mass index as a predictive factor of periodontal therapy outcomes. J Dent Res. 2014;93(1):49-54. doi: 10.1177/0022034513511084. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034513511084
Gul SS, Imran NK, Al-Sharqi AJB, Abdulkareem AA. Association of overweight/obesity with the severity of periodontitis using BPE code in an Iraqi population. Clin Epidemiol Global Health. 2020;9. doi: 10.1016/j.cegh.2020.06.005. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cegh.2020.06.005
Ismail H, Mahmood M. Effect of melatonin supplementation on the gingival health and lipid profiles in obese periodontitis patients. J Baghdad Coll Dentistry. 2022;34:51-59. DOI: https://doi.org/10.26477/jbcd.v34i1.3092
Fain JN, Madan AK, Hiler ML, Cheema P, Bahouth SW. Comparison of the release of adipokines by adipose tissue, adipose tissue matrix, and adipocytes from visceral and subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissues of obese humans. Endocrinology. 2004;145(5):2273-2282. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-1336. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2003-1336
Ameen EM, Mohammed HY. Correlation between tumor necrosis factor–alfa and anti-tyrosine phosphatase with obesity and diabetes type 2. Iraqi J Sci. 2022;63(8):3322-3331. doi: 10.24996/ijs.2022.63.8.7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.24996/ijs.2022.63.8.7
Yamazaki K, Yoshie H, Seymour GJ. T cell regulation of the immune response to infection in periodontal diseases. Histol Histopathol. 2003;18(3):889-896. doi: 10.14670/HH-18.889.
Grewal IS, Flavell RA. CD40 and CD154 in cell-mediated immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:111-35. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.16.1.111. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.16.1.111
Chaturvedi R, Gupta M, Jain A, Das T, Prashar S. Soluble CD40 ligand: a novel biomarker in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. Clin Oral Investig. 2015;19(1):45-52. doi: 10.1007/s00784-014-1216-3. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-014-1216-3
Freedman JE. CD40-CD40L and platelet function: beyond hemostasis. Circ Res. 2003;92(9):944-946. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000074030.98009.FF. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000074030.98009.FF
Tenovuo J, Lagerlof F, (Eds.), Textbook of clinical cardiology, (2nd ed.), 1994, Munksgaard Copenhagen: Munksgaard Copenhagen. 1994;17-43.
Nuttall FQ. Body mass index: Obesity, BMI, and health: A critical review. Nutr Today. 2015;50(3):117-128. doi: 10.1097/NT.0000000000000092. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/NT.0000000000000092
Tonetti MS, Greenwell H, Kornman KS. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J Periodontol. 2018;89(Suppl 1):S159-S172. doi: 10.1002/JPER.18-0006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.18-0006
Chapple ILC, Mealey BL, Van Dyke TE, Bartold PM, Dommisch H, Eickholz P, et al. Periodontal health and gingival diseases and conditions on an intact and a reduced periodontium: Consensus report of workgroup 1 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J Periodontol. 2018;89(Suppl 1):S74-S84. doi: 10.1002/JPER.17-0719. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.17-0719
Papapanagiotou D, Nicu EA, Bizzarro S, Gerdes VE, Meijers JC, Nieuwland R, et al. Periodontitis is associated with platelet activation. Atherosclerosis. 2009;202(2):605-611. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.05.035. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.05.035
Marcaccini AM, Meschiari CA, Sorgi CA, Saraiva MC, de Souza AM, Faccioli LH, et al. Circulating interleukin-6 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein decrease after periodontal therapy in otherwise healthy subjects. J Periodontol. 2009;80(4):594-602. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.080561. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2009.080561
Schönbeck U, Mach F, Libby P. CD154 (CD40 ligand). Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2000;32(7):687-693. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(00)00016-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1357-2725(00)00016-9
Zhou L, Stordeur P, de Lavareille A, Thielemans K, Capel P, Goldman M, et al. CD40 engagement on endothelial cells promotes tissue factor-dependent procoagulant activity. Thromb Haemost. 1998;79(5):1025-1028. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1615114
Silva TA, Garlet GP, Fukada SY, Silva JS, Cunha FQ. Chemokines in oral inflammatory diseases: apical periodontitis and periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 2007;86(4):306-319. doi: 10.1177/154405910708600403. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/154405910708600403
Schönbeck U, Mach F, Sukhova GK, Murphy C, Bonnefoy JY, Fabunmi RP, Libby P. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells by T lymphocytes: a role for CD40 signaling in plaque rupture? Circ Res. 1997;81(3):448-454. doi: 10.1161/01.res.81.3.448. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.81.3.448
Alhashimi N, Frithiof L, Brudvik P, Bakhiet M. CD40-CD40L expression during orthodontic tooth movement in rats. Angle Orthod. 2004;74(1):100-105. doi: 10.1043/0003-3219(2004)074<0100:CEDOTM>2.0.CO;2.
Sempowski GD, Chess PR, Moretti AJ, Padilla J, Phipps RP, Blieden TM. CD40 mediated activation of gingival and periodontal ligament fibroblasts. J Periodontol. 1997;68(3):284-292. doi: 10.1902/jop.1997.68.3.284. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.1997.68.3.284
Recker EN, Brogden KA, Avila-Ortiz G, Fischer CL, Pagan-Rivera K, Dawson DV, et al. Novel biomarkers of periodontitis and/or obesity in saliva-An exploratory analysis. Arch Oral Biol. 2015;60(10):1503-1509. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.07.006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.07.006
Wassenaar A, Verschoor T, Kievits F, Den Hartog MT, Kapsenberg ML, Everts V, et al. CD40 engagement modulates the production of matrix metalloproteinases by gingival fibroblasts. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999;115(1):161-167. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00764.x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00764.x
Herzberg MC, Weyer MW. Dental plaque, platelets, and cardiovascular diseases. Ann Periodontol. 1998;3(1):151-160. doi: 10.1902/annals.1998.3.1.151. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1902/annals.1998.3.1.151
André P, Nannizzi-Alaimo L, Prasad SK, Phillips DR. Platelet-derived CD40L: the switch-hitting player of cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2002 Aug 20;106(8):896-9. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000028962.04520.01. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000028962.04520.01
Unek IT, Bayraktar F, Solmaz D, Ellidokuz H, Sisman AR, Yuksel F, et al. The levels of soluble CD40 ligand and C-reactive protein in normal weight, overweight and obese people. Clin Med Res. 2010;8(2):89-95. doi: 10.3121/cmr.2010.889. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3121/cmr.2010.889
Wakai K, Kawamura T, Umemura O, Hara Y, Machida J, Anno T, et al. Associations of medical status and physical fitness with periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1999;26(10):664-672. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051x.1999.261006.x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-051X.1999.261006.x
Christan C, Dietrich T, Hägewald S, Kage A, Bernimoulin JP. White blood cell count in generalized aggressive periodontitis after non-surgical therapy. J Clin Periodontol. 2002 Mar;29(3):201-6. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051x.2002.290303.x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-051x.2002.290303.x
Guldiken S, Demir M, Arikan E, Turgut B, Azcan S, Gerenli M, et al. The levels of circulating markers of atherosclerosis and inflammation in subjects with different degrees of body mass index: Soluble CD40 ligand and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. Thromb Res. 2007;119(1):79-84. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2005.12.019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2005.12.019
Desideri G, Ferri C. Effects of obesity and weight loss on soluble CD40L levels. JAMA. 2003;289(14):1781-1782. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.14.1781. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.14.1781
Schernthaner GH, Kopp HP, Krzyzanowska K, Kriwanek S, Koppensteiner R, Schernthaner G. Soluble CD40L in patients with morbid obesity: significant reduction after bariatric surgery. Eur J Clin Invest. 2006;36(6):395-401. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2006.01649.x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.2006.01649.x
Furukawa S, Fujita T, Shimabukuro M, Iwaki M, Yamada Y, Nakajima Y, Nakayama O, Makishima M, Matsuda M, Shimomura I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2004;114(12):1752-61. doi: 10.1172/JCI21625. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI21625
Davì G, Guagnano MT, Ciabattoni G, Basili S, Falco A, Marinopiccoli M, et al. Platelet activation in obese women: role of inflammation and oxidant stress. JAMA. 2002;288(16):2008-2014. doi: 10.1001/jama.288.16.2008. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.288.16.2008
Lehmann AP, Nijakowski K, Swora-Cwynar E, Łuczak J, Czepulis N, Surdacka A. Characteristics of salivary inflammation in obesity. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2020;130(4):297-303. doi: 10.20452/pamw. DOI: https://doi.org/10.20452/pamw.15186
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 )

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Published by Al-Rafidain University College. This is an open access journal issued under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/).











