Evaluating TLR4 Gene Expression to Monitor Disease Progression in Iraqi Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54133/ajms.v5i1S.382Keywords:
DAS28, Rheumatoid arthritis, Real time PCR, TLR4 geneAbstract
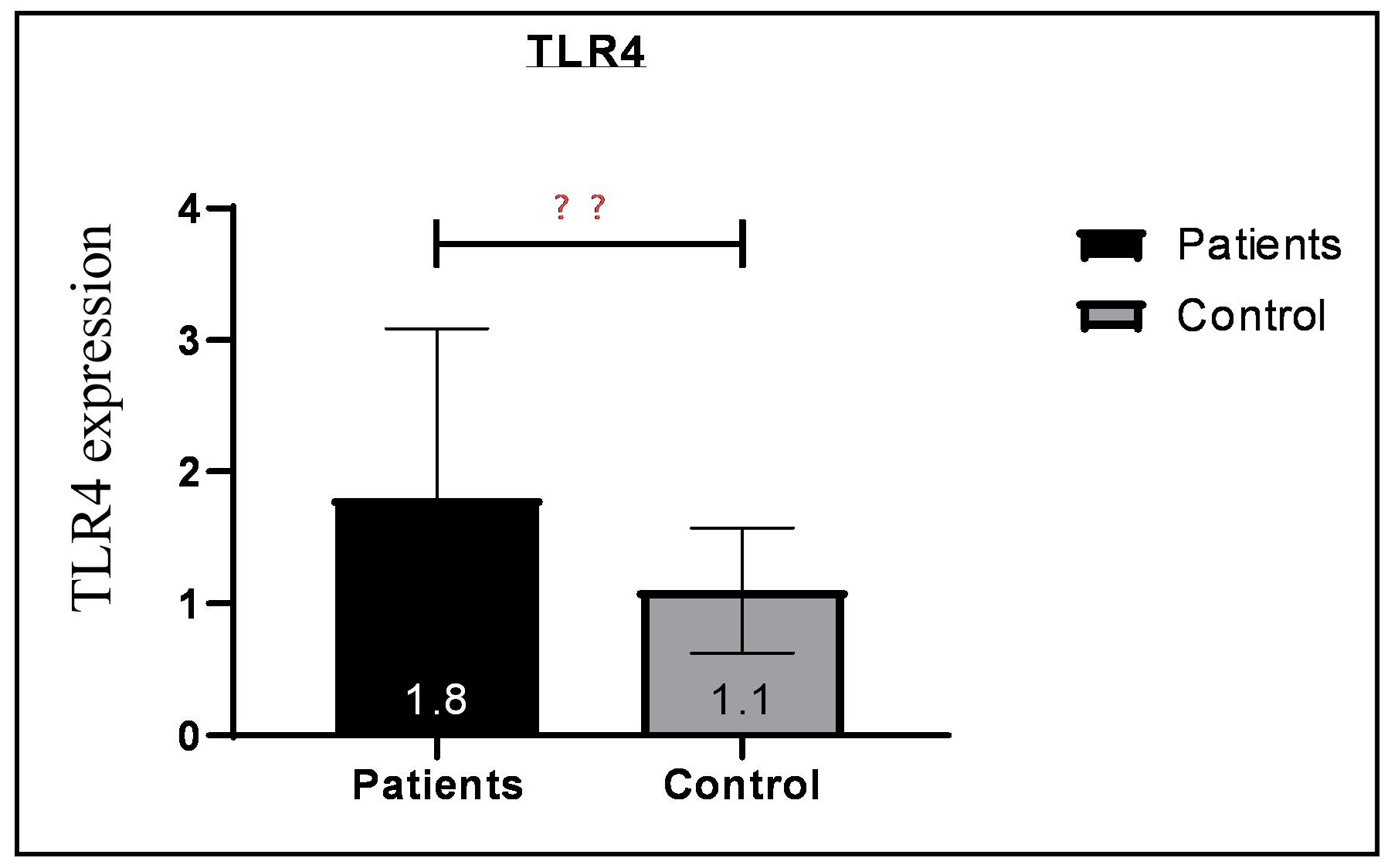
Background: Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a significant role in the activation of adaptive immunity and may have an essential role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Objectives: To assess the gene expression of TLR4 in individuals with RA compared to healthy individuals. Methods: From July to December 2022. A total of 100 individuals were encompassed in the study, consisting of 50 individuals diagnosed with RA, of whom 42 were females and 8 were males, with an average age of 45.22 years. Additionally, there were 50 healthy control participants, 40 of whom were females and 10 were males, with an average age of 45.64 years. To assess the TLR4 transcript levels, blood samples were collected from each participant, and RNA extraction was performed. cDNA synthesis was carried out, and real-time PCR was utilized for the analysis. The researchers also assessed the clinicopathological characteristics of the patients. Results: The serum TLR4 gene was significantly overexpressed in RA patients (fold change 2.59) compared to the controls (fold change 1.07). The expression level of the TLR4 gene was correlated with the clinicopathological characteristics of the patients, including erythrocyte sedimentation rates (ESR), RF, anti-CCP antibody, and DAS28. Conclusion: TLR4 was overexpressed in RA patients and was correlated with disease activity. It might be a therapeutic target and may contribute to the pathogenesis of RA.
Downloads
References
Al-Hashimi NH, Al-Gebori AM, Alosami MHM. Evaluation of the human pulmonary activation-regulated chemokine (CCL18/PARC) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels in Iraqi patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Iraqi J Sci. 2020:713-719. doi: 10.24996/ijs.2020.61.4.1.
Al_Badran AHK, Algabri HC, Al Saeedi KRH, Alqazzaz AM. Incidence of rheumatoid arthritis at Marjan Teaching Hospital in Babylon, Iraq (2014–2019). Med J Babylon. 2022;19(3):358. doi: 10.4103/MJBL.MJBL_32_22.
Al Ghuraibawi ZAG, Sharquie IK, Gorial FI. A novel link of serum IL-39 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Iraqi J Sci. 2023:1651-1661 doi: 10.24996/ijs.2023.64.4.8.
Duan T, Du Y, Xing C, Wang HY, Wang R-F. Toll-like receptor signaling and its role in cell-mediated immunity. Front Immunol. 2022;13:812774. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.812774.
Sameer AS, Nissar S. Toll-like receptors (TLRs): structure, functions, signaling, and role of their polymorphisms in colorectal cancer susceptibility. BioMed Res Int. 2021;2021. doi: 10.1155/2021/1157023.
Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4(7):499-511. doi: 10.1038/nri1391.
Barreto G, Manninen M, K. Eklund K. Osteoarthritis and toll-like receptors: when innate immunity meets chondrocyte apoptosis. Biology. 2020;9(4):65. doi: 10.3390/biology9040065.
Szebeni B, Veres G, Dezsofi A, Rusai K, Vannay A, Mraz M, et al. Increased expression of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4 in the colonic mucosa of children with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;151(1):34-41. doi: 10.1007/s12016-019-08742-z.
Hänninen MM, Haapasalo J, Haapasalo H, Fleming RE, Britton RS, Bacon BR, et al. Expression of iron-related genes in human brain and brain tumors. BMC Neurosci. 2009;10(1):1-9. doi:10. 1016/j.autrev.2016.12.003.
AL-Faisal AHM, Alfartusi A. Expression of APEX1 gene in specimens of Iraqi patients with lung cancer. Int J ChemTech Res. 2017,10(3): 613-621.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402-408. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03531.
Elmalt HA, Ibrahim AM, Girgiss MW. MicroRNA-146a expression and serum interleukin-17 level as potential biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis. Egypt J Chem. 2021;64(7):3423-3429. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-10-36.
Hassoon HJ, Jasim WE, Abbas AAH. The evaluation of some biomarkers according to rheumatoid factor in early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis from Iraqi patients. Iraqi J Sci. 2020:2196-203. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262.
Chiad IA, Yossef HS, Al-Saidi MA, Abbas MA. Evaluation of some immunological markers in the rheumatoid arthritis patients. Iraqi J Sci. 2015;56(3C):2488-2493. doi: 10.21608/ejchem.2021.62848.3355.
Eser B, Sahin N. Evaluation of tool-like receptor-2 and 4 and interleukin-6 gene expressions in Turkish rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35:2693-2697. doi: 10.24996/ijs.2020.61.9.6.
Radstake TR, Roelofs MF, Jenniskens YM, Oppers-Walgreen B, van Riel PL, Barrera P, et al. Expression of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in rheumatoid synovial tissue and regulation by proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-12 and interleukin-18 via interferon-gamma. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(12):3856-3865. doi: 10.1002/art.20678.
Salim R, Hassan T, Elnady B. MIR-146A and TLR4 gene expression in predicting rheumatoid arthritis disease. Egypt J Biochem Mol Biol. 2017;35(1-2):55-77. doi: 10.1007/s10067-016-3282-1.
Arleevskaya MI, Larionova R, Brooks WH, Bettacchioli E, Renaudineau Y. Toll-like receptors, infections, and rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rev Aller Immunol. 2020;58:172-181. doi: 10.1002/art.20678.
Elshabrawy HA, Essani AE, Szekanecz Z, Fox DA, Shahrara S. TLRs, future potential therapeutic targets for RA. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16(2):103-113. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2016.12.003.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 )

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Published by Al-Rafidain University College. This is an open access journal issued under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/).











