Estimation of Tenascin-C Levels in Iraqi Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54133/ajms.v5i1S.273الكلمات المفتاحية:
Diabetic nephropathy، Extracellular matrix، Tenascin-C، Type 2 diabetesالملخص
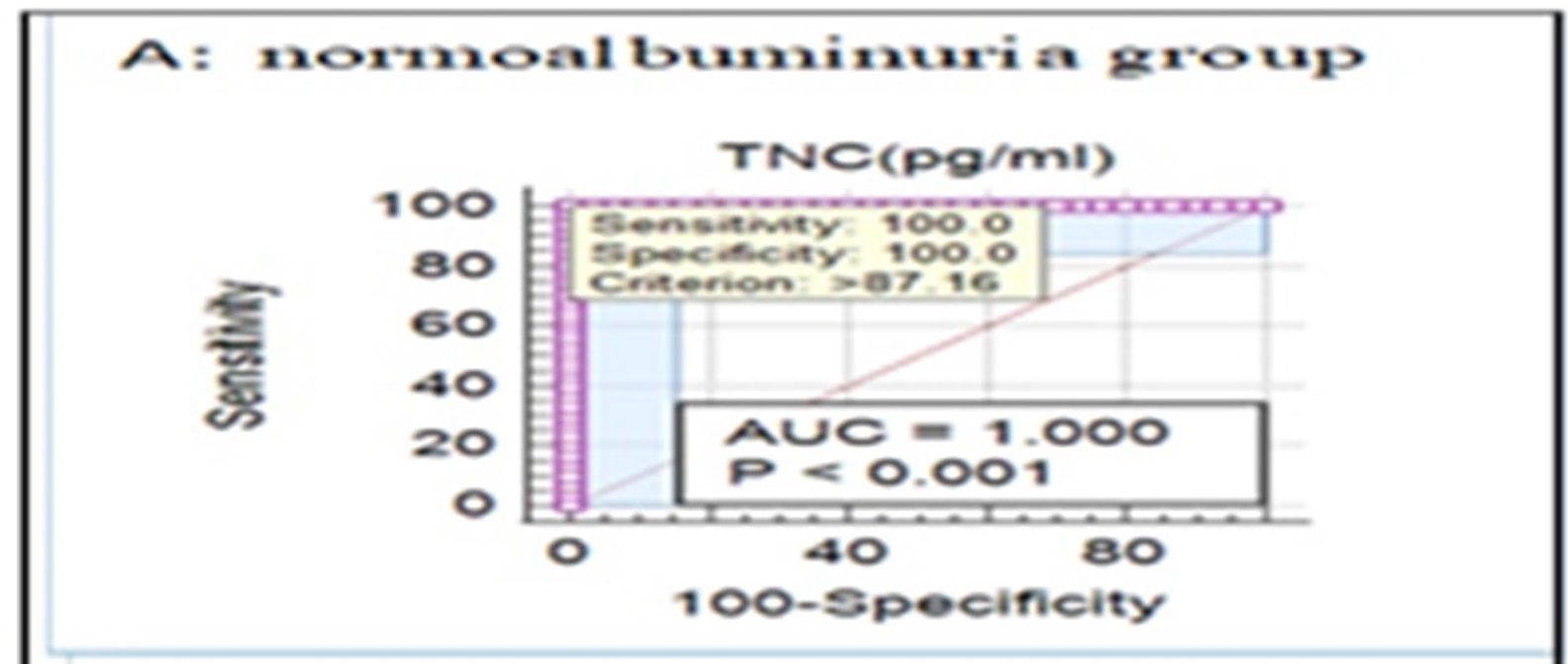
الخلفية: يحدث مرض الكلى في المرحلة النهائية (ESRD) في الغالب بسبب اعتلال الكلية السكري (DN) (1)، وهو أحد أكثر عواقب الأوعية الدموية الدقيقة المزمنة المروعة لمرض السكري. كان الهدف من هذا البحث هو تحديد العلاقة بين Tenascin-C (TNC) واعتلال الكلية السكري وكذلك مستوى TNC في مراحل مختلفة من هذه التسبب. الطرق والمواد: شملت 90 مريضاً من مرضى T2DM و30 شخصاً يبدو أنهم في حالة جيدة. اعتمادًا على نسبة الألبومين إلى الكرياتينين (ACR) ((البيلة الألبومينية الطبيعية، والبيلة الألبومينية الدقيقة، والبيلة الألبومينية الكبيرة))، تم تقسيم مجموعات المرضى إلى ثلاث فئات. تم استخدام مجموعة ELISA لتحديد تركيز TNC في الدم. النتائج: في هذه الدراسة، اكتشفنا فروق ذات دلالة إحصائية أعلى بين مستويات TNC وFBG وTC وTGs وHDL وLDL وVLDL في مرضى اعتلال الكلية السكري مقارنة بالأشخاص الأصحاء، وكذلك بين مستويات TNC ووظائف الكلى في المرضى الذين يعانون من مراحل مختلفة. من التسبب في المرض. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، اكتشفنا وجود علاقة إيجابية كبيرة بين TNC ومستويات الكرياتينين واليوريا وACR في الدم. الاستنتاجات: من النتائج، يمكن استنتاج أن TNC قد يكون مرتبطا بتطور المرض وقد يكون المؤشر الأكثر دقة لاعتلال الكلية السكري.
التنزيلات
المراجع
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157(2019):107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843.
Atlas D. International diabetes federation (IDF), 2015.
Mayer-Davis EJ, Lawrence JM, Dabelea D, Divers J, Isom S, Dolan L, et al. Incidence trends of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among youths, 2002-2012. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(15):1419-1429. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1610187.
Oost LJ, van der Heijden AAWA, Vermeulen EA, Bos C, Elders PJM, Slieker RC, et al. Serum magnesium is inversely associated with heart failure, atrial fibrillation, and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(8):1757-1765. doi: 10.2337/dc21-0236.
Aikaeli F, Njim T, Gissing S, Moyo F, Alam U, Mfinanga SG, et al. Prevalence of microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes in low-and-middle-income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Glob Public Health. 2022;2(6):1-21. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0000599.
Saputro SA, Pattanaprateep O, Pattanateepapon A, Karmacharya S, Thakkinstian A. Prognostic models of diabetic microvascular complications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 2021;10(288):1-11. doi: 10.1186/s13643-021-01841-z.
Jitraknatee J, Ruengorn C, Nochaiwong S. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetes patients: A cross-sectional study in primary care practice. Sci Rep. 2020;1(10):6205. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63443-4.
Farhan LO, Dawood A, Abed BA. Comparison study between adipsin levels in sera of Iraqi patients with diabetes and neuropathy. Baghdad Sci J. 2023;20(3):726-733. doi: 10.21123/bsj.2022.7408.
Harding JL, Pavkov ME, Magliano DJ, Shaw JE, Gregg EW. Global trends in diabetes complications: a review of current evidence. Diabetologia. 2019;62(1):3-16. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4711-2.
Rao V, Rao ALBV, Hong S, Candasamy M, Kumar S. Diabetic nephropathy: An update on pathogenesis and drug development. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev. 2019;13(1):754-762. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2018.11.054.
Gnudi L, Long DA, (Eds.), Diabetic Nephropathy: Methods and Protocols, MIMB, volume 2067, Springer; 2020. Available from: http://www.springer.com/series/7651
Tucker RP, Degen M. Revisiting the tenascins: Exploitable as cancer targets? Front Oncol. 2022;12:908247. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.908247.
Aubert A, Mercier-Gouy P, Aguero S, Berthier L, Liot S, Prigent L, et al. Latent TGF-β activation is a hallmark of the Tenascin family. Front Immunol. 2021;12:613438. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.613438.
Li M, Wu M, Zhu H, Hua Y, Ma Z, Yao J, et al. Serum tenascin-C and alarin levels are associated with cardiovascular diseases in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Endocrinol. 2022;2022:2009724. doi: 10.1155/2022/2009724.
Draicchio F, Behrends V, Tillin NA, Hurren NM, Sylow L, Mackenzie R. Involvement of the extracellular matrix and integrin signaling proteins in skeletal muscle glucose uptake. J Physiol. 2022;600(20):4393-4408. doi: 10.1113/JP283039.
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Kang J, Wang Q, First T. Metformin regulates inflammation and fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease through TNC/TLR4/NF-κB/miR-155-5p inflammatory loop. World J Diabetes. 2021;12(1):19-46. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i1.19.
Kiss A, Nadasy GL, Fees A, Arnold Z, Aykac I, Dostal C, et al. Alterations in coronary resistance artery network geometry in diabetes and the role of tenascin C. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023;24(1):6. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2401006.
Sharma A, Arora D, (Eds.), Role of Inflammation in Diabetic Retinopathy. In: Diabetic Eye Disease. 2021. p. 1–24.
Singh R, Mugale MN. Global recurrence rates in diabetic nephropathy: A pathological systematic review. United J Qual Valid. 2021;2(1):1-8.
Ansar MM, Shahrokhirad R, Lebady MK. Risk factors of microalbuminuria and macroalbuminuria in type 2 diabetic patients in north of Iran - Rasht. Nephrourol Mon. 2017;9(1):e40031. doi: 10.5812/numonthly.40031.
Sosale B, Sosale AR, Chandrashekara S, Panchagnula R, Dey S, Prasannakumar KM. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on reduction of cardiometabolic risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2018;38(2):221-227. doi: 10.1007/s13410-017-0584-z.
Asbaghi O, Fouladvand F, Moradi S, Ashtary-Larky D, Choghakhori R, Abbasnezhad A. Effect of green tea extract on lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev. 2020;14(4):293-301. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.03.018.
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Groop L, Henry RR, Herman WH, Holst JJ, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2015;1:1-23. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2015.19.
Dixit AK, Dey R, Suresh A, Chaudhuri S, Panda AK, Mitra A, et al. The prevalence of dyslipidemia in patients with diabetes mellitus of ayurveda Hospital. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2014;13(1):58. doi: 10.1186/2251-6581-13-58.
Yang H, Young D, Gao J, Yuan Y, Shen M, Zhang Y, et al. Are blood lipids associated with microvascular complications among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients? A cross-sectional study in Shanghai, China. Lipids Health Dis. 2019;18(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-0970-2.
Nezami N, Ghorbanihaghjo A, Argani H, Safa J, Rashtchizadeh N. Lovastatin enhances paraoxonase enzyme activity and quells low-density lipoprotein susceptibility to oxidation in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Clin Biochem. 2011;44(2-3):165-170. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2010.10.006.
Kanagala P, Arnold JR, Khan JN, Singh A, Gulsin GS, Chan DCS, et al. Plasma tenascin-C: A prognostic biomarker in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Biomarkers. 2020;25(7):556-565. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2020.1810319.
Yokokawa T, Sugano Y, Nakayama T, Nagai T, Matsuyama T, Ohta-Ogo K, et al. Significance of myocardial Tenascin-C expression in left ventricular remodeling and long-term outcome in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur J of Heart Fail. 2016;18(4):375-385. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.464.
Xie Q, Zang M, Mao X, Xu M, Liu S, Shang D, et al. Matrix protein Tenascin-C promotes kidney fibrosis via STAT3 activation in response to tubular injury. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(12):1044. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05496-z.
Liabeuf S, Barreto DV, Kretschmer A, Barreto FC, Renard C, Andrejak M, et al. High circulating levels of large splice variants of Tenascin-C is associated with mortality and cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease patients. Atherosclerosis. 2011;215(2011):116-124. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.11.038.
التنزيلات
منشور
كيفية الاقتباس
إصدار
القسم
الرخصة
الحقوق الفكرية (c) 2023 Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences

هذا العمل مرخص بموجب Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Published by Al-Rafidain University College. This is an open access journal issued under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/).










