تحضير وتقييم جل العين الموضعي بآلية تحفيز مزدوجة لتوصيل جاتيفلوكساسين وبيتاميثازون فوسفات الصوديوم
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54133/ajms.v6i2.597الكلمات المفتاحية:
Betamethasone، Drug delivery، Gatifloxacin، Gellan gum، In situ ophthalmic gel، Poloxamerالملخص
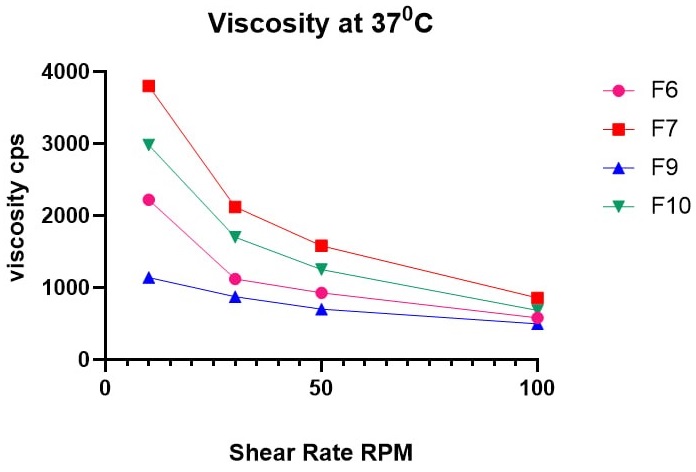
تتمثل التحديات الرئيسية التي يواجهها علماء الصياغة في التوصيل البصري في الإزالة السريعة قبل القرنية والتطبيق المتعدد، خاصة مع الأدوية المضادة للميكروبات. تهدف هذه الدراسة إلى تطوير هلام عيني في الموقع يستخدم كلاً من الآليات المستحثة بالأيونات والحساسة للحرارة لتحقيق الجيل. تم تحضير صيغ تحتوي على نسب مختلفة من البولوكسامير 407 وصمغ الجيلان (F1-F24) ومقارنتها فيما يتعلق بدرجة حرارة التبلور، قدرة التبلور، زمن التبلور، ودراسة الإطلاق والتخلل. تم اختبار الصيغة المثلى فيما يتعلق بتساوي التوتر، ومضادات الميكروبات، والتهيج في الأرانب. تتراوح درجة الحموضة في التركيبات من 6.7 إلى 7.3. المستحضرات التي اجتازت اختبار درجة حرارة التبلور بنجاح هي F6 وF7 وF9 وF10. وتراوحت نسبة المحتوى الدوائي لكلا العقارين (F6، F7، F9، F10) من 98.64% إلى 99.95%. في الموقع، أظهرت المواد الهلامية (F6، F7، F9، وF10) سلوكًا ريولوجيًا متدفقًا كاذبًا أو ترقق القص، كما يتضح من انخفاض اللزوجة مع زيادة السرعة الزاوية. الصيغة المثالية (F7) التي تحتوي على 17% بولوكسامير و0.5% صمغ جيلان حصلت على 15 ثانية من وقت التبلور عند 34 درجة مئوية وبقيت على شكل هلام لمدة 270 دقيقة. لقد كان متساوي التوتر ولم تظهر خلايا الدم الحمراء أي تغيير في الحجم والشكل عند تطبيق الجل في الموقع. تم تمديد إطلاق كلا العقارين ولم يلاحظ أي تهيج في عين الأرنب عند اختباره على الحيوانات. من خلال تحسين فترة الإقامة قبل القرنية والتوافر البيولوجي للعين نتيجة للإدارة الأقل تواترا، يمكن اعتبار تركيبة الجل الجديدة في الموقع بديلا متفوقا لقطرات العين التقليدية من جاتيفلوكساسين وبيتاميثازون لالتهابات العين.
التنزيلات
المراجع
Gaballa SA, Kompella UB, Elgarhy O, Alqahtani AM, Pierscionek B, Alany RG, et al. Corticosteroids in ophthalmology: drug delivery innovations, pharmacology, clinical applications, and future perspectives. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021;11(3):866-893. doi: 10.1007/s13346-020-00843-z.
Peter M, Panonnummal R. A Review on newer ocular drug delivery systems with an emphasis on glaucoma. Adv Pharm Bull. 2021;11(3):399-413. doi: 10.34172/apb.2021.048.
Kalam MA, Sultana Y, Samad A, Ali A, Aqil M, Sharma M, et al. Gelrite‐based in vitro gelation ophthalmic drug delivery system of gatifloxacin. J Dispers Sci Technol. 2008;29(1):89-96. doi: 10.1080/01932690701688482.
Shaikh DA, Momin MMJDDL. Formulation and evaluation of ion-triggered in situ gel for effective ocular delivery of ciprofloxacin HCl and olopatadine HCl in combination. Drug Deliv Lett. 2024;14(1):49-66. doi: 10.2174/0122103031267809231128111259.
Jumelle C, Gholizadeh S, Annabi N, Dana R. Advances and limitations of drug delivery systems formulated as eye drops. J Control Release. 2020;321:1-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.01.057.
Tagalpallewar A, Rai P, Polshettiwar S, Manish W, Baheti A. Formulation, optimization and evaluation of ion triggered ophthalmic in situ gel. J Pharm Res Int. 2021;33(28A):58-77. doi: 10.9734/jpri/2021/v33i28A31511.
Saini R, Saini S, Singh G, Banerjee A. In situ gels-a new trends in ophthalmic drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2015;6:386-390.
Gözcü S, Polat HK, Gültekin Y, Ünal S, Karakuyu NF, Şafak EK, et al. Formulation of hesperidin-loaded in situ gel for ocular drug delivery: a comprehensive study. J Sci Food Agric. 2024. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13407.
Gupta B, Mishra V, Gharat S, Momin M, Omri A. Cellulosic polymers for enhancing drug bioavailability in ocular drug delivery systems. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021;14(11):1201. doi: 10.3390/ph14111201.
Szalai B, Jójárt-Laczkovich O, Kovács A, Berkó S, Balogh GT, Katona G, Budai-Szűcs M. Design and optimization of in situ gelling mucoadhesive eye drops containing dexamethasone. Gels. 2022;8(9):561. doi: 10.3390/gels8090561.
Padmasri B, Nagaraju R, Prasanth D. A comprehensive review on in situ gels. Int J Appl Pharm. 2020;12(6):24-33. doi: 10.22159/ijap.2020v12i6.38918.
Dewan M, Sarkar G, Bhowmik M, Das B, Chattoapadhyay AK, Rana D, Chattopadhyay D. Effect of gellan gum on the thermogelation property and drug release profile of Poloxamer 407 based ophthalmic formulation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;102:258-265. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.03.194.
Yang H, Ding S, Fan D, Zhu Z, Fan Y, Li J, Wang D. Design and evaluation of a dual-sensitive in situ gel for the controlled release of pranoprofen. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024;25(2):35. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02748-3.
Yu S, Zhang X, Tan G, Tian L, Liu D, Liu Y, et al. A novel pH-induced thermosensitive hydrogel composed of carboxymethyl chitosan and poloxamer cross-linked by glutaraldehyde for ophthalmic drug delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;155:208-217. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.073.
Joshi PH, Youssef AAA, Ghonge M, Varner C, Tripathi S, Dudhipala N, et al. Gatifloxacin loaded nano lipid carriers for the management of bacterial conjunctivitis. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023;12(8):1318. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12081318.
Sabry HS, Al-Shohani ADH, Mahmood SZ. Formulation and evaluation of levofloxacin and betamethasone ophthalmic emulgel. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021;13(2):205-211. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_338_20.
Kolawole OM, Cook MT. In situ gelling drug delivery systems for topical drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2023;184:36-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2023.01.007.
Huang Y, Yang N, Zhang Y, Hou J, Gao Y, Tian L, et al. The gelling behavior of gellan in the presence of different sodium salts. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;193(Pt A):768-777. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.173.
Sun J, Zhou Z. A novel ocular delivery of brinzolamide based on gellan gum: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022;16:4109-4110. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S153405.
Al-Bazzaz FY, Al-Kotaji M. Ophthalmic in-situ sustained gel of ciprofloxacin, preparation and evaluation study. Int J App Pharm. 2018;10(4):153-161. doi: 10.22159/ijap.2018v10i4.26885.
Kalaria VJ, Saisivam S, Alshishani A, Aljariri Alhesan JS, Chakraborty S, Rahamathulla M. Design and evaluation of in situ gel eye drops containing nanoparticles of Gemifloxacin Mesylate. Drug Deliv. 2023;30(1):2185180. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2023.2185180.
Kapoor A, Gupta G. Optimization and characterization of ion activated ocular in-situ gel formulation for bacterial conjunctivitis. Int J Appl Pharm. 2020:182-91. doi: 10.22159/ijap.2020v12i4.37925.
Amer Z, Mahdi Z, Alhamdany A. Formulation and evaluation of ocular in-situ gelling system containing ciprofloxacin and naproxen sodium. Res J Pharm Technol. 2021;14:91-95. doi: 10.5958/0974-360X.2021.00017.2.
Mohammadi M, Patel K, Alaie SP, Shmueli RB, Besirli CG, Larson RG, et al. Injectable drug depot engineered to release multiple ophthalmic therapeutic agents with precise time profiles for postoperative treatment following ocular surgery. Acta Biomater. 2018;73:90-102. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.04.037.
Arora K, Singh LJJoPNR. Formulation development and characterization of in situ gel containing bimatoprost for the treatment of glaucoma. J Pharm Negative Results. 2023:1986-2001. doi: 10.47750/pnr.2023.14.02.247.
Majeed A, Khan N. Ocular in situ gel: An overview. J Drug Deliv Ther. 2019;9:337-347. doi: 10.22270/jddt.v9i1.2231.
Abbas MN, Khan SA, Sadozai SK, Khalil IA, Anter A, Fouly ME, et al. Nanoparticles loaded thermoresponsive in situ gel for ocular antibiotic delivery against bacterial keratitis. Polymers. 2022;14(6):1135. doi: 10.3390/polym14061135.
Maddiboyina B, Jhawat V, Desu PK, Gandhi S, Nakkala RK, Singh S. Formulation and evaluation of thermosensitive flurbiprofen in situ nano gel for the ocular delivery. J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 2021;32(12):1584-1597. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2021.1927460.
Pramanik A, Sahoo R, Nanda A, Pattnaik K, Mallick S. Swelling kinetics and corneal hydration level of kaolinin-HPMC hydrogel film. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2020;82(2):306-314.
Arthanari S, Mani G, Jang JH, Choi JO, Cho YH, Lee JH, et al. Preparation and characterization of gatifloxacin-loaded alginate/poly (vinyl alcohol) electrospun nanofibers. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016;44(3):847-852. doi: 10.3109/21691401.2014.986676.
Zhang Y, Wu X, Li H, Du N, Song S, Hou W. Preparation and characterization of (betamethasone sodium phosphate intercalated layered double hydroxide)@liposome nanocomposites. Colloid Surfaces A: Physicochem Engineer Aspects. 2017;529:824-831. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.06.063.
Tassew NG, Laing ST, Aaronson J, de Jong I, Schuetz C, Lorget F. Tolerability assessment of formulation pH in New Zealand white rabbits following intravitreal administration. Toxicol Pathol. 2021;49(3):605-609. doi: 10.1177/0192623320969667.
Zahir-Jouzdani F, Wolf JD, Atyabi F, Bernkop-Schnürch A. In situ gelling and mucoadhesive polymers: why do they need each other? Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2018;15(10):1007-1019. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2018.1517741.
Morsi N, Ibrahim M, Refai H, El Sorogy H. Nanoemulsion-based electrolyte triggered in situ gel for ocular delivery of acetazolamide. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017;104:302-314. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2017.04.013.
Vigani B, Rossi S, Sandri G, Bonferoni MC, Caramella CM, Ferrari F. Recent advances in the development of in situ gelling drug delivery systems for non-parenteral administration routes. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(9):859. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12090859.
Vyas U, Gehalot N, Jain V, Mahajan SC. A Review on in situ gelling system for ophthalmic drug delivery. Curr Res Pharm Sci. 2021;11(4):98-106. doi: 10.24092/CRPS.2021.110402.
Sha G, Liu J, Jiang Z, Zhu M, Zhu Y, Gu C, et al. In situ gels: The next new frontier in ophthalmic drug delivery system. Polymer Adv Technol. 2023;34(8): 2646-2662. doi: 10.1002/pat.6079.
Pandya AK, Vora LK, Umeyor C, Surve D, Patel A, Biswas S, et al. Polymeric in situ forming depots for long-acting drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023;200:115003. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2023.115003.
Kurniawansyah IS, Rusdiana T, Sopyan I, Desy Arya IF, Wahab HA, Nurzanah D. Comparative study of in situ gel formulation based on the physico-chemical aspect: Systematic review. Gels. 2023;9(8):645. doi: 10.3390/gels9080645.
Stachowiak N, Kowalonek J, Kozlowska J, Burkowska-But A. Stability studies, biodegradation tests, and mechanical properties of sodium alginate and gellan gum beads containing surfactant. Polymers. 2023;15(11):2568. doi: 10.3390/polym15112568.
de Oliveira Cardoso VM, Kiraly VTR, Boni FI, Ferreira NN, Ferreira LMB, Pereira FMV, et al. Rational design of nanocarriers based on gellan gum/retrograded starch exploiting polyelectrolyte complexation and ionic cross-linking processes: A potential technological platform for oral delivery of bevacizumab. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2021;66:102765. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2021.102765.
Nagesh C, Patil M, Chandrashekhara S, Sutar R. A novel in situ gel for sustained ophthalmic delivery of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride and dexamethasone-design and characterization. Der Pharmacia Lett. 2012;4(3):821-827.
Almeida H, Amaral MH, Lobão P, Lobo JM. In situ gelling systems: a strategy to improve the bioavailability of ophthalmic pharmaceutical formulations. Drug Discov Today. 2014;19(4):400-412. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2013.10.001.
التنزيلات
منشور
كيفية الاقتباس
إصدار
القسم
الرخصة
الحقوق الفكرية (c) 2024 Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences

هذا العمل مرخص بموجب Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Published by Al-Rafidain University College. This is an open access journal issued under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/).










