تقييم نشاط التئام الجروح وتحفيز موت الخلايا المبرمج لمشتقات الكينازولينون الجديدة
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54133/ajms.v6i2.640الكلمات المفتاحية:
: موت الخلايا المبرمج , سرطان الثدي,السمية الخلوية,سرطان الغدة الرئوية, اختبار الخدش.الملخص
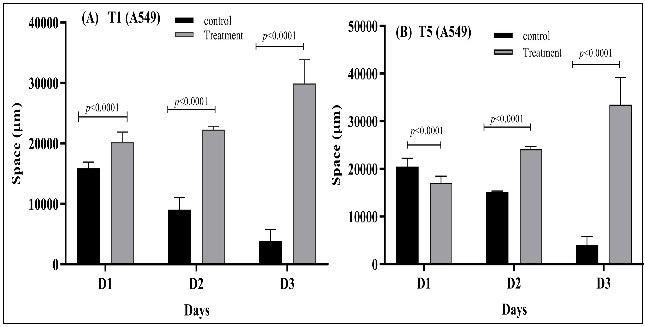
الخلفية: غالبًا ما يستخدم علاج السرطان بأدوية العلاج الكيميائي مع طرق أخرى كجزء من النظام العلاجي القياسي. من المعروف أن النشاط المضاد للأورام للعديد من عوامل العلاج الكيميائي يرتبط بقدراتها على إحداث موت الخلايا المبرمج. أظهرت المركبات التي تعتمد على الكينازولينون أنشطة ملحوظة في خطوط الخلايا السرطانية المختلفة ، وبالتالي تمثل سقالات واعدة في تصميم محفزات موت الخلايا المبرمج. الأهداف :للتحقق في ما يلي: (1) تقييم قدرات مشتقات الكينازولينون المُصنَّعة مؤخرًا (M1 و M2) [9، 10] لإيقاف التئام الجروح (2) قدرة المركبات المُصنَّعة على تحفيز موت الخلايا المبرمج في خطوط الخلايا السرطانية المختارة عن طريق باستخدام أكريدين البرتقالي / يوديد البروبيديوم (AO / PI) صبغة مزدوجة. الطريقة: في هذا البحث تم اختبار اثنين من مشتقات الكينازولينون (M1 و M2) لقدرتهما على إيقاف التئام الجروح والحث على موت الخلايا المبرمج باستخدام خطين من الخلايا السرطانية ، خط خلايا سرطان الثدي (MCF-7) وخط خلايا سرطان الرئة (A549). النتائج: اظهرت المركبات قدرة عالية على تحفيز موت الخلايا المبرمج وثبطت بشكل معنوي التئام الجروح في كلا خطوط الخلايا السرطانية.
التنزيلات
المراجع
Khazir J, Hyder I, Gayatri JL, Prasad Yandrati L, Nalla N, et al. Design and synthesis of novel 1,2,3-triazole derivatives of coronopilin as anti-cancer compounds. Eur J Med Chem. 2014;82:255-262. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.05.053.
Fox JL, MacFarlane M. Targeting cell death signaling in cancer: minimizing 'collateral damage'. Br J Cancer. 2016;115(1):5-11. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.111.
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ. Cell death: critical control points. Cell. 2004;116(2):205-219. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00046-7.
Radhi AK, Al-Shawi NN. Possible protective effects of high- versus low- dose of lutein in combination with irinotecan on liver of rats: Role of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Indian J Forens Med Toxicol. 2021;15 (1):2439-2445. doi: 10.37506/ijfmt.v15i1.13767.
Lopez J, Tait SWG. Mitochondrial apoptosis: Killing cancer using the enemy within. Br J Cancer. 2015;112(6):957-962. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.85.
Radhi AK, Al-Shawi NN. Possible protective effects of lutein against ciprofloxacin induced bone marrow toxicity in rats. Iraqi J Pharm Sci. 2021;30(1):233-239. doi: 10.31351/vol30iss1pp233-2396.
Liu Y, Zhu X. Endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria tethering in neurodegenerative diseases. Transl Neurodegener. 2017;6:21. doi: 10.1186/s40035-017-0092-6.
Bao H, Zhang Q, Zhu Z, Xu H, Ding F, Wang M, et al. BHX, a novel pyrazoline derivative, inhibits breast cancer cell invasion by reversing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and down-regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):9153. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09655-7.
Radhi AK, Al-Shawi NN, Faris AH. Impact of Omega 3 on the Genotoxicity of Irinotecan on Bone Marrow and Spleen of Rats: in-vivo Study. Iraqi J Pharm Sci. 2023; 32(1): 53-58. doi: 10.31351/vol32iss1pp53-58.
Gatadi S, Pulivendala G, Gour J, Malasala S, Bujji S, Parupalli R, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of new 4(3H)-Quinazolinone derivatives as potential anticancer agents. J Mol Str. 2020;1200:127097. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127097.
Oleiwi MA, Zalzala MH. Synthesis, molecular docking study and cytotoxicity evaluation of some quinazolinone derivatives as nonclassical antifolates and potential cytotoxic agents. Iraqi J Pharm Sci. 2022;31:2. doi: 10.31351/vol31iss2pp283-296.
Oleiwi MA, Zalzala MH, Mohammed MH. Synthesis, cytotoxicity evaluation and molecular docking simulation of some new 4-(3H)-Quinazolinone-thiadiazole hybrids as anticancer agents. Pak J Med Health Sci. 2022;16(3):697-702. doi: 10.53350/pjmhs22163697.
Al-Shammari AM, Alshami MA, Umran MA, Almukhtar AA, Yaseen NY, Raad K, et al. Establishment and characterization of a receptor-negative, hormone-nonresponsive breast cancer cell line from an Iraqi patient. Breast Cancer. 2015;7:223-230. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S74509.
Bobadilla AVP, Arévalo J, Sarró E, Byrne HM, Maini PK, Carraro T, et al. In vitro cell migration quantification method for scratch assays. J R Soc Interface. 2019;16(151):20180709. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2018.0709.
Al-Shammari AM, Abdullah AH, Allami ZM, Yaseen NY. 2-Deoxyglucose and Newcastle disease virus synergize to kill breast cancer cells by inhibition of glycolysis pathway through glyceraldehyde3-phosphate downregulation. Front Mol Biosci. 2019;6:90. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00090.
Mohammed MS, Al-Taee MF, Al-Shammari AM. Caspase dependent and independent anti-hematological malignancy activity of AMHA1 attenuated Newcastle disease virus. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2019;8(3):211-223. doi: 10.22088/IJMCM.BUMS.8.3.211.
Jabir MS, Taha AA, Sahib UI, Taqi ZJ, Al-Shammari AM, Salman AS. Novel of nano delivery system for Linalool loaded on gold nanoparticles conjugated with CALNN peptide for application in drug uptake and induction of cell death on breast cancer cell line. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;94:949-964. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.10.014.
Ataollahi E, Behrouz M, Mardaneh P, Emami M, Zare S, Zafarian H, et al. Novel quinazolinone derivatives as anticancer agents: Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and computational studies. J Mol Struc. 2024;1295, Part 2:136622. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.136622.
Dahabiyeh LA, Hourani W, Darwish W, Hudaib F, Abu-Irmaileh B, Deb PK, et al. Molecular and metabolic alterations of 2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one derivatives in prostate cancer cell lines. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):21599. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26148-4.
Faraj FL, Zahedifard M, Paydar M, Looi CY, Abdul Majid N, Ali HM, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and anticancer activity of new quinazoline derivatives against MCF-7 cells. Sci World J. 2014;2014:212096. doi: 10.1155/2014/212096.
التنزيلات
منشور
كيفية الاقتباس
إصدار
القسم
الرخصة
الحقوق الفكرية (c) 2024 Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences

هذا العمل مرخص بموجب Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Published by Al-Rafidain University College. This is an open access journal issued under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/).










